Difference between revisions of "WordPress Toolkit"
(→Managing WordPress Instances) |
m |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
* On the remaining three tabs you can manage the instance’s plugins, themes, and change the database username and password. | * On the remaining three tabs you can manage the instance’s plugins, themes, and change the database username and password. | ||
| − | + | == Removing and Detaching Instances == | |
You can detach WordPress instances that you do not want to see and manage in WordPress Toolkit. Detaching does not remove the instance, merely hides it from WordPress Toolkit. A detached instance will be attached to WordPress Toolkit again after you scan for WordPress instances. You can detach WordPress instances individually or multiple instances at a time. | You can detach WordPress instances that you do not want to see and manage in WordPress Toolkit. Detaching does not remove the instance, merely hides it from WordPress Toolkit. A detached instance will be attached to WordPress Toolkit again after you scan for WordPress instances. You can detach WordPress instances individually or multiple instances at a time. | ||
| − | + | === To detach WordPress instances === | |
# To to WordPress, choose one or more instances you want to detach, and then click the [[File:Menu_Button.png]] button (to detach an individual instance) or click Detach (to detach multiple instances). | # To to WordPress, choose one or more instances you want to detach, and then click the [[File:Menu_Button.png]] button (to detach an individual instance) or click Detach (to detach multiple instances). | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
#: Unlike detaching, removing completely deletes a WordPress instance. You can remove WordPress instances individually or multiple instances at a time. | #: Unlike detaching, removing completely deletes a WordPress instance. You can remove WordPress instances individually or multiple instances at a time. | ||
| − | + | === To remove WordPress instances === | |
# Go to WordPress, choose one or more instances you want to delete, and then click the [[File:Menu_Button.png]] button (to remove an individual instance) or click Remove (to remove multiple instances). | # Go to WordPress, choose one or more instances you want to delete, and then click the [[File:Menu_Button.png]] button (to remove an individual instance) or click Remove (to remove multiple instances). | ||
# Click Remove. | # Click Remove. | ||
| − | + | === Search Engine Indexing and Debugging === | |
By default, a newly created WordPress Toolkit website is shown in search results of search engines. If your website is not yet ready for public viewing, switch off Search engine indexing. | By default, a newly created WordPress Toolkit website is shown in search results of search engines. If your website is not yet ready for public viewing, switch off Search engine indexing. | ||
If you are installing WordPress for testing or development, you can enable Debugging to automatically find and fix errors in the website code. To do so, click "Setup" next to “Debugging”, select the WordPress debugging tools you want to activate, and then click OK. | If you are installing WordPress for testing or development, you can enable Debugging to automatically find and fix errors in the website code. To do so, click "Setup" next to “Debugging”, select the WordPress debugging tools you want to activate, and then click OK. | ||
Revision as of 16:40, 27 December 2018
Contents
This page is under construction
WordPress Toolkit
Through XMission’s Shared Hosting Platform we have the WordPress Toolkit enabled on all our servers. This Toolkit is a single management interface that allows you to easily install, configure, and manage your WordPress Development.
Installing WordPress
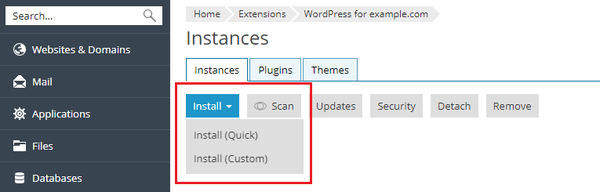
To install a new WordPress instance, go to WordPress and click Install. The following installation options are available:
- Install (Quick). This will install the newest version of WordPress, and use WordPress default settings. The new instance will be available via HTTPS for each domain as SSL Protection is become required for all hosting.
- Install (Custom) (XMission recommends using this option). This allows you to set up the administrator user, select the desired WordPress version, HTTP/HTTPS, specify the database name, select auto-update settings, and more.
To view a list of all installations attached to the WordPress Toolkit, go to Websites & Domains > WordPress.
Managing WordPress Instances
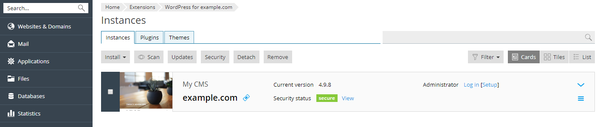
Go to WordPress to see all WordPress instances hosted on the server. WordPress Toolkit groups information about each instance in a card.
The individual cards will contain a screenshot and a number of controls that give you easy access to frequently used tools. The screenshot is real time and should reflect the current home page of your website. If you click the screenshot of the website, the Open Site button appears. Click the button to open the website in a new browser tab.
Security
WordPress development is frequently attacked by hackers. To help prevent compromises the Toolkit analyzes how safe your instance is. After analyzing your site you’ll be able to see the result below the screenshot of the website:
If you see “warning” or “danger” next to one of these aspects, click “View” and fix it.
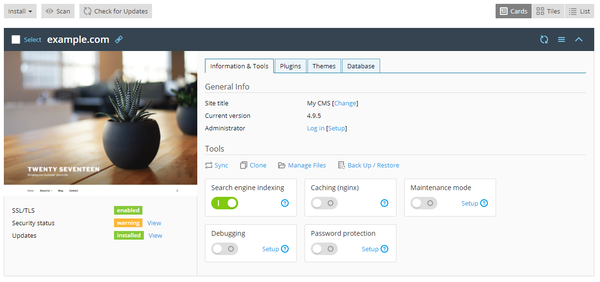
General Information
In the “General Info” section, you see the WordPress website’s title and its WordPress version. Here you can:
- Click “Change” next to the default “My CMS” title to give your website a custom name.
- Click “Log in” to log in to WordPress as an administrator.
- Click “Setup” next to “Log in” to change general WordPress settings.
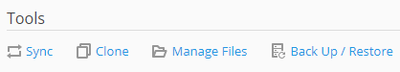
Tools
In the “Tools” section, click to access the following WordPress Toolkit features:
- “Sync” to synchronize the content of your website with another one.
- “Clone” to make a full copy of your website.
- “Manage Files” to manage the website’s files in File Manager.
- “Back Up/Restore” to create a backup of your website and restore it if necessary.
The controls below give you easy access to the following settings and tools:
- “Search engine indexing” shows your website in search results of search engines.
- "Caching (nginx)" speeds up the website load time and reduces server load.
- “Debugging” helps you debug a website that is not ready for viewing and being tested or developed.
- “Maintenance mode” hides your website’s content from visitors.
- "Password Protection" specifies the password you will use to log in to WordPress from Plesk.
- On the remaining three tabs you can manage the instance’s plugins, themes, and change the database username and password.
Removing and Detaching Instances
You can detach WordPress instances that you do not want to see and manage in WordPress Toolkit. Detaching does not remove the instance, merely hides it from WordPress Toolkit. A detached instance will be attached to WordPress Toolkit again after you scan for WordPress instances. You can detach WordPress instances individually or multiple instances at a time.
To detach WordPress instances
- To to WordPress, choose one or more instances you want to detach, and then click the
 button (to detach an individual instance) or click Detach (to detach multiple instances).
button (to detach an individual instance) or click Detach (to detach multiple instances). - Click Detach.
- Unlike detaching, removing completely deletes a WordPress instance. You can remove WordPress instances individually or multiple instances at a time.
To remove WordPress instances
- Go to WordPress, choose one or more instances you want to delete, and then click the
 button (to remove an individual instance) or click Remove (to remove multiple instances).
button (to remove an individual instance) or click Remove (to remove multiple instances). - Click Remove.
Search Engine Indexing and Debugging
By default, a newly created WordPress Toolkit website is shown in search results of search engines. If your website is not yet ready for public viewing, switch off Search engine indexing.
If you are installing WordPress for testing or development, you can enable Debugging to automatically find and fix errors in the website code. To do so, click "Setup" next to “Debugging”, select the WordPress debugging tools you want to activate, and then click OK.