Router and Wireless Troubleshooting: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Is Your Router Getting Power?= | =Is Your Router Getting Power?= | ||
Revision as of 11:39, 21 March 2017
Is Your Router Getting Power?
Most people will leave their routers in a location that is rarely visited. It's possible that your router has somehow lost power. Check to see if you see any LEDs lighting up, indicating that the router has a power source.
Can You Ping Your Router?
From your computer, try to ping your router, also known as your gateway. This may appear to be complex and technical, but in fact it is very simple to achieve.
Windows
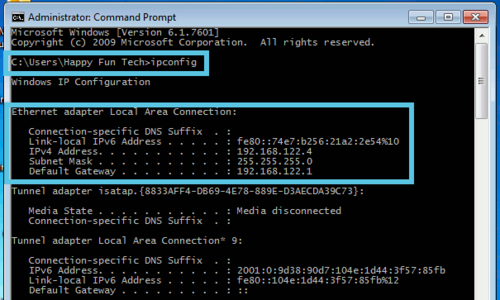
1. Open the command prompt (Using the start menu's search ability, search for "Command Prompt") and type in "ipconfig". This will show you all of your networking configurations. If your computer uses an ethernet cable, look for "Ethernet adapter". If you use wifi, look for "Wireless Adapter".
2. Once you have more information, you will be able to see if you have an IP address or not. It will normally appear as a 192.168.x.x address.
- In our example, our IP address is 192.168.122.4 and our gateway is 192.168.122.1. This will vary from computer to computer, but the premise remains the same. If you have an IP address, that means at the very least there is a connection from your computer, to your router. The gateway is your router.
3. To ping your router, type ping 192.168.1.1 (or whatever your gateway IP address is).
- Likewise, you can ping google by executing the command ping 8.8.8.8. This will show if your computer has Internet access, as well as a router connection.
Mac and Linux
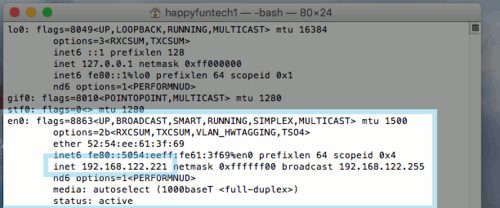
1. Open the command prompt by using the spotlight magnifying class in the top right corner. Search for "terminal" and open the command prompt. Once you have the terminal open, type in the command "ifconfig". This will show you your network interfaces and the IP address your computer has assigned to it.
2. Next we will execute a command called ping which will tell us if your Mac is connected successfully to your router. Type the command ping 192.168.1.1 then press enter.
- In our example, our IP address is 192.168.122.221. This will vary from computer to computer, but the premise remains the same. If you have an IP address, that means at the very least there is a connection from your computer, to your router. The gateway is your router.
3. If your ping responds successfully, you are connected to your router correctly. If you get no response, your router may be turned off, or a cable is disconnected between your computer and your router.
- Likewise, you can ping google by executing the command ping 8.8.8.8. This will show if your computer has Internet access, as well as a router connection.
Try from Multiple Computers
It is entirely possible that the problem you are encountering is an issue local to the computer or device you are using. Try using something else to see if multiple devices and computers are experiencing the same issue with your network.
Verify Your Cables Are Correctly Secured
Your cables may have been accidentally tugged on at some point, pulling them loose from your router. Always check your cables connections by reconnecting them and listing for the audible click they produce. Check on both sides of the cable in case only one side was impacted.
Check for Overheating
Is your router/modem getting hot to the touch? If so, it's possible that it may be defunct. Warm devices are not always worrisome, but if the router is irritatingly hot, leave it unplugged for a few minutes to cool down. Once it is cooled off, plug it back in and monitor it for the next few hours to see if the temperature rises again. If you think your device is malfunctioning, contact your router manufacturer.
Reconfigure your WiFi to use a different Channel
[to do]
Reposition the Router
1. Avoid Enclosed Spaces
Your router creates a frequency around itself that if you could see it, would look like a donut emitting from the antenna. With this in mind, keep it out of places that are closed off, and remote from where you plan to use your WiFi. The more open, the better!
2. Keep it Out of the Kitchen
Your router creates a frequency that is shared with many other devices. Such as your microwave. Keep the two away from each other to prevent them from fighting with each other for dominance.
3. Try to Place it in an Open Room/Environment
Keep your router away from exterior walls, and basements. If you plan on using your WiFi in the center of your home, your router being on the opposite side of the house will do little to help increase it's performance.
4. Be Aware of Your Homes Construction
- Metal / Load bearing walls / Concrete / Plumbing
Like enclosed spaces, your Router will have a hard time penetrating through thick objects. Some of the most common problems are what is behind your walls, out of your sight. Ventilation shafts and plumbing can prevent the frequency from passing through and into your device.
5. Use Your Antennas To Your Advantage
Your Router emits a mesh of information that radiates outwards from the antenna(s). It would look like a large cloud-like donut, with a hole in the top and bottom, where the tip and base of the antenna is. Since most new routers have multiple antennas, move them and arrange them to create a larger area of impact to cover your home more thoroughly.
Check for a Firmware Update
[to do]
Reset to Factory Defaults
[to do]