Router and Wireless Troubleshooting: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
===DHCP - Dynamic IP=== | ===DHCP - Dynamic IP=== | ||
Customers that haven't requested a static IP or purchased a subnet will use this connection type. | Customers that haven't requested a static IP or purchased a subnet will use this connection type. | ||
* Many routers' configuration wizards will be able to detect this and connect automatically | * Many routers' configuration wizards will be able to detect this and connect automatically | ||
| Line 159: | Line 161: | ||
===DHCP - Static IP or Subnet=== | ===DHCP - Static IP or Subnet=== | ||
Customers that have requested DHCP for static IPs or purchased subnets will use this connection type. | Customers that have requested DHCP for static IPs or purchased subnets will use this connection type. | ||
* Routes the static IP or subnet using the MAC address of the customer's device | * Routes the static IP or subnet using the MAC address of the customer's device | ||
| Line 170: | Line 174: | ||
===PPPoE - Static IP or Subnet=== | ===PPPoE - Static IP or Subnet=== | ||
Customers who have requested a static IP address or have purchased a subnet will use this connection type unless they have requested otherwise. | Customers who have requested a static IP address or have purchased a subnet will use this connection type unless they have requested otherwise. | ||
* Username and password are required | * Username and password are required | ||
| Line 184: | Line 190: | ||
===Choosing a Router=== | ===Choosing a Router=== | ||
Router models are as diverse as the homes, apartments, and offices for which they provide a network. For most situations our recommended routers in the section below will be ideal, though a four-story home may need something more robust than a one bedroom apartment or small office so asking the following questions will help you determine which router model will best suit your needs. | Router models are as diverse as the homes, apartments, and offices for which they provide a network. For most situations our recommended routers in the section below will be ideal, though a four-story home may need something more robust than a one bedroom apartment or small office so asking the following questions will help you determine which router model will best suit your needs. | ||
1. Do I need a router or a switch, or neither? | 1. Do I need a router or a switch, or neither? | ||
| Line 203: | Line 211: | ||
* Most major manufacturers are comparable, deciding on which model and price-tier of router will be the greater determining factor in router performance. | * Most major manufacturers are comparable, deciding on which model and price-tier of router will be the greater determining factor in router performance. | ||
3. Where should I install the router? | 3. Where should I install the router? | ||
Revision as of 04:04, 19 November 2018
Is Your Router Getting Power?
Most of the time a reboot can often resolve:
- network issues
- poor website connections
- slow speeds
- dropped connections
Doing an occasional reboot keeps the router acting like new. The reboot process is simple:
- Unplug your router’s power cable.
- Wait 60 seconds then plug the power back in.
Note: Rebooting your router more than 2-4 times a month could indicate a firmware update is required. See information below regarding firmware upgrades.
Check for Overheating
Electronic devices, including routers, can overheat. Overheating can cause damage to the hardware, slowing your Internet connection.
Check your router’s temperature. If it seems very hot to the touch, ensure:
- There is airflow allowing it to keep cool.
- The routers vents are not blocked or covered.
- The router is not located around a heated surface (hidden behind a TV).
Verify Your Cables Are Correctly Secured
Often, a pet or household member can accidentally pull on or kick out a cable. Loose or damaged cables can cause issues with your router.
To troubleshoot this:
- Check all of the cables and ensure they are securely connected.
- Check the power cables as well. Loose plugs at the wall can create power surges that can damage your router.
- Check to make sure each end of the Ethernet cable is securely connected. If you are unsure, unplug the Ethernet cable and plug it back in. You should hear a click sound when plugged in correctly.
Can You Ping Your Router?
From your computer, try to ping your router, also known as your gateway. This may appear to be complex and technical, but in fact it is very simple to achieve.
Windows
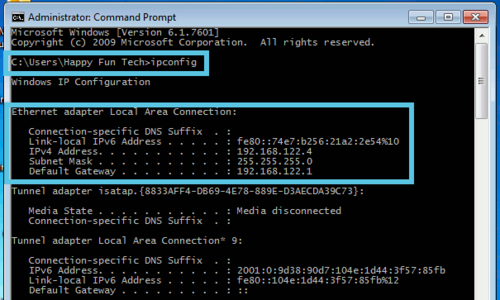
1. Open the command prompt (Using the start menu's search ability, search for "Command Prompt") and type in "ipconfig". This will show you all of your networking configurations. If your computer uses an ethernet cable, look for "Ethernet adapter". If you use wifi, look for "Wireless Adapter".
2. Once you have more information, you will be able to see if you have an IP address or not. It will normally appear as a 192.168.x.x address.
- In our example, our IP address is 192.168.122.4 and our gateway is 192.168.122.1. This will vary from computer to computer, but the premise remains the same. If you have an IP address, that means at the very least there is a connection from your computer, to your router. The gateway is your router.
3. To ping your router, type ping 192.168.1.1 (or whatever your gateway IP address is).
- Likewise, you can ping google by executing the command ping 8.8.8.8. This will show if your computer has Internet access, as well as a router connection.
Mac and Linux
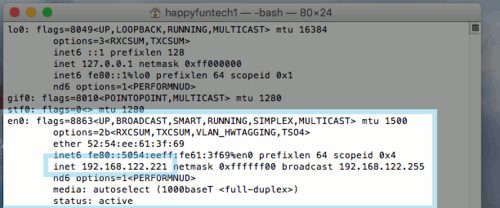
1. Open the terminal by using the spotlight magnifying glass in the top right corner. Search for "terminal" and open the terminal. Once you have the terminal open, type in the command "ifconfig". This will show you your network interfaces and the IP address your computer has assigned to it.
2. Next we will execute a command called ping which will tell us if your Mac is connected successfully to your router. Type the command ping 192.168.1.1 then press enter.
- In our example, our IP address is 192.168.122.221. This will vary from computer to computer, but the premise remains the same. If you have an IP address, that means at the very least there is a connection from your computer, to your router. The gateway is your router.
3. If your ping responds successfully, you are connected to your router correctly. If you get no response, your router may be turned off, or a cable is disconnected between your computer and your router.
- Likewise, you can ping google by executing the command ping 8.8.8.8. This will show if your computer has Internet access, as well as a router connection.
Try from Multiple Computers
It is entirely possible that the problem you are encountering is an issue local to the computer or device you are using. Try using something else to see if multiple devices and computers are experiencing the same issue with your network.
Re-position the Router
- Avoid enclosed spaces
- Your router creates a frequency around itself that if you could see it, would look like a doughnut emitting from the antenna. With this in mind, keep it out of places that are closed off and remote from where you plan to use your WiFi. The more open, the better!
- Keep it out of the kitchen
- Your router creates a frequency that is shared with many other devices, like your microwave. Keep the two away from each other to prevent them from fighting with each other for dominance.
- Move your router to a central location
- Keep your router away from exterior walls, and basements. If you plan on using your WiFi in the center of your home, your router being on the opposite side of the house will do little to help increase it's performance.
- Be aware of your homes construction
- Metal / Load bearing walls / Concrete / Plumbing
- Like enclosed spaces, your Router will have a hard time penetrating through thick objects. Some of the most common problems are what is behind your walls, out of your sight. Ventilation shafts and plumbing can prevent the frequency from passing through and into your device.
- Use your antennas to your advantage
- Your Router emits a mesh of information that radiates outwards from the antenna(s). It would look like a large cloud-like doughnut, with a hole in the top and bottom, where the tip and base of the antenna is. Since most new routers have multiple antennas, move them and arrange them to create a larger area of impact to cover your home more thoroughly.
Reconfigure your WiFi to use a different channel
If your router is located around a lot of other nearby wireless connections (like inside an apartment building), you may be getting interference from your neighbors.
To change your wireless channel:
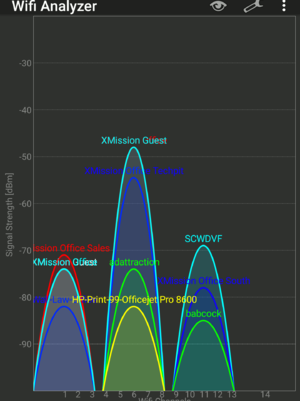
- Using an Android device (if you have one), use the Wi-Fi Analyzer app to find a less used Wi-Fi channel in your home.
- Change the wireless channel in your router’s interface to the suggested channel from the analyzer.
Apple does not offer any type of WiFi analyzer at the moment. The below screen shot is from an android device running Wifi Analyzer from the Google Play Store.
Also note some routers have built in analyzer that can be used as well.
Check for a Firmware Update
CAUTION:
If you do not know how to do this, please refer to your router manual before proceeding.
Flashing a firmware incorrectly can damage your router and cause it to be inoperable.
Your router may still be on the factory default firmware version that it was purchased with. Manufacturers tend to release updates to their routers to increase security, and resolve potention service problems. Upgrading your firmware is a great idea to try when troubleshooting your wireless, or any other router related problems.
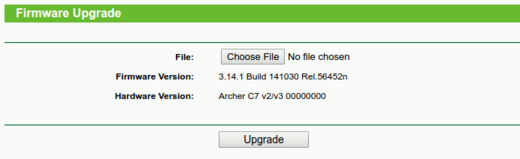
To Check and Upgrade your Firmware:
- Login to your Routers Administration Webpage. Some routers will require you to use a URL like, http://routerlogin.net. Others tends to be 192.168.1.1 or sometimes 192.168.0.1. The username and password can be found on the sticker under your router, or in the guide it came with. If you cannot obtain it either way, look online for your specific routers default login information.
- Find your routers Firmware settings. This tends to be in the Administration section of the ADVANCED menu.
- Your Router should have notes on this page detailing steps to go about searching for a new firmware version. If you have an internet connection, you may also have a "Check" button that will allow the router to lookup the newest firmware version and help install it.
- If you do not have any help notes on how to proceed with a firmware upgrade, go to the support section of your router manufacturers website, and find your specific router. Then under the support options, you should find files for new firmware files.
- Double check to see if your version is lower/older, and not the same as the current version available. If it is not, download the file.
- If you have the firmware file downloaded, using the same router administration firmware upgrade page, use the "Choose File" to upload the new firmware file to the router. Once you have the new file selected, proceed by clicking "Upload" or "Next".
- Wait for the process to complete, and test out your new firmware for your router to see if your issues have been resolved.
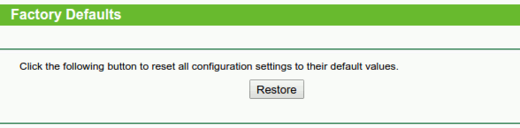
Reset to Factory Defaults
Features built into the router could also be slowing you down. By default, any feature that can monitor or slow your connection is disabled. To ensure something wasn’t enabled by mistake, you can do a factory reset on your router. We recommend using this step as a last resort.
A factory reset will require a reconfiguration of your router (like you did back when you first got it). It will include setting up your wireless network name and passphrase again.
Note: You can use the same network name and passphrase. It doesn’t require a custom one each time you decide to do a reset.
To factory reset(Refer to your router manual or online instructions) :
- Locate the reset button, usually a small pinhole, on the back of your router.
- Using a paperclip or something similar, you’ll insert the end into the reset hole and hold for about 30 seconds.
- Normally, you will see the lights on your router flash or go out. This is an indication that you have successfully reset your router.
There are countless other issues that would make your router not operate correctly. Outside of the listed steps above, it is possible that your computer may have related problems where additional troubleshooting is needed. Contact a trusted computer technician to help determine if there are hardware or software issues playing a part in your troubles.
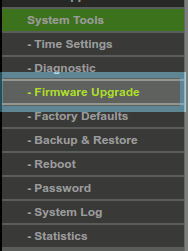
Some routers will give you the option from inside the admin panel, while others will have a physical button that needs to be pressed. For this example, it can be found under System tools then Factory Defaults.
Connection Types
DHCP - Dynamic IP
Customers that haven't requested a static IP or purchased a subnet will use this connection type.
- Many routers' configuration wizards will be able to detect this and connect automatically
- Sometimes referred to as 'dynamic' or 'automatic'
DHCP - Static IP or Subnet
Customers that have requested DHCP for static IPs or purchased subnets will use this connection type.
- Routes the static IP or subnet using the MAC address of the customer's device
- Select type 'DHCP' 'dynamic' or 'automatic'
- The static IP or subnet will only be routed if the MAC address on the device matches the MAC address in our configuration file, when connecting a new device please reach out to our support team so that we can update the MAC address and ensure the static routes are maintained
PPPoE - Static IP or Subnet
Customers who have requested a static IP address or have purchased a subnet will use this connection type unless they have requested otherwise.
- Username and password are required
- If you aren't sure of your login credentials, please do not hesitate to reach out to our support department
Recommended Routers & Configuration
Choosing a Router
Router models are as diverse as the homes, apartments, and offices for which they provide a network. For most situations our recommended routers in the section below will be ideal, though a four-story home may need something more robust than a one bedroom apartment or small office so asking the following questions will help you determine which router model will best suit your needs.
1. Do I need a router or a switch, or neither?
- The UTOPIA fiber gateway delivers your connection over a single ethernet port, typically GE1 or LAN1 though the number may vary depending on your setup. To split this connection up to more than one device you will need to purchase a router. Most routers will provide your wireless network as well as multiple ethernet ports to which you can connect other devices.
- A network switch can split the connection from the router up to even more devices. If you need more ethernet connections than your router provides, you can add a network switch. NOTE: The router must always come 'first,' with the switch then plugged into the router. Plugging a switch directly into the UTOPIA gateway will not properly split your connection and may cause loopback problems.
2. What speed is my connection?
- While most gigabit routers will provide more than enough bandwidth over an ethernet connection to your devices that use a wired connection, the strength of the WiFi signal varies from model to model, as does the number of wireless antennae.
- Devices that connect over wired ethernet will have the fastest most reliable connection. Using ethernet wherever possible frees up your WiFi network to feed the devices which do not have ethernet ports.
- How many devices will be using WiFi? How many will be using wired ethernet? Will I need extreme wireless coverage or will moderate be enough for my smart phones and tablets?
- Most major manufacturers are comparable, deciding on which model and price-tier of router will be the greater determining factor in router performance.
3. Where should I install the router?
- WiFi signals come up from your router in the shape of an ice-cream cone, so placing it at the bottom of your desired coverage area is preferable.
- Interference can affect WiFi performance, keep the router as far away from other electronic devices as possible.
Recommended Routers
NETGEAR R7000 Nighthawk AC1900 Smart WiFi Router
Second Generation Broadcom 802.11ac AC1900 router with storage sharing, USB 2.0 & 3.0 ports, and OpenDNS based parental controls.

- Full manual: https://www.downloads.netgear.com/files/GDC/R7000/R7000_IG_6pgCover+Interior_28May2014.pdf
- Default wireless network: (written on router's label)
- Address: 192.168.1.1 or http://www.routerlogin.net
- Username: admin
- Password: password
TP-LINK Archer AC3150 Wireless MU-MIMO Router
AC3100 (aka 3150) class router with gigabit ethernet ports and USB 3.0 storage and printer sharing

- Default Wireless Network: (starts with "TP-Link_..." written on router's label)
- Address: 192.168.0.1 or http://tplinkwifi.net
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
ASUS RT-AC68U Wireless-AC1900 Dual Band Router
Second generation Broadcom-based AC1900 router with USB 2.0 & 3.0, drive and printer sharing, and PPTP VPN server

- Default wireless network: (starts with "ASUS..." written on router's label)
- Address: 192.168.1.1 or http://router.asus.com
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
NETGEAR R7800 Nighthawk X4S Smart WiFi Gaming Router
QCA based 4x4 MU-MIMO router with gigabit ethernet ports, USB 3.0 and eSATA storage and printer sharing, and 160 MHz mode support

- Default wireless network: (written on router's label)
- Address: 192.168.1.1 or http://www.routerlogin.net
- Username: admin
- Password: password
TP-LINK Archer C5 V2 AC1200 Dual Band Gigabit Router
Broadcom-based AC1200 router with gigabit ethernet ports and USB 2.0 storage and printer sharing, a complete redesign from version 1

- Default Wireless Network: (starts with "TP-LINK_..." written on router's label)
- Address: 192.168.0.1 or http://tplinkwifi.net
- Username: admin
- Password: admin